Use Cases
Image Retrieval
Image Metadata Retrieval with ThanoSQL
Introduction
Managing and retrieving large image datasets is a common challenge for photographers, art galleries, and companies involved in poster production or exhibitions. This use case will guide you through the process of using ThanoSQL to handle and query large datasets of images and their metadata. By the end of this use case, you will be able to search for images based on both image and text inputs and retrieve detailed metadata about the images, such as dimensions and photographer information.This tutorial can be executed both within ThanoSQL Lab and in a local Python/Jupyter environment. Whether you prefer to work directly within ThanoSQL Lab’s integrated environment or set up a local development environment on your machine, the instructions provided will guide you through the necessary steps.
If you want to try running the code from this use case, you can download the complete Jupyter notebook using this link: Download Jupyter Notebook. Alternatively, you can download it directly to your machine using the
wget command below:To run the models in this tutorial, you will need the following tokens:
- OpenAI Token: Required to access all the OpenAI-related tasks when using OpenAI as an engine. This token enables the use of OpenAI’s language models for various natural language processing tasks.
- Huggingface Token: Required only to access gated models such as Mistral on the Huggingface platform. Gated models are those that have restricted access due to licensing or usage policies, and a token is necessary to authenticate and use these models. For more information, check this Huggingface documentation. Make sure to have these tokens ready before proceeding with the tutorial to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted workflow.
Dataset
We will be working with two datasets:Unsplash Embedding Sample Table (unsplash_embed_sample)
Unsplash Embedding Sample Table (unsplash_embed_sample)
Contains detailed metadata about the images including information about the photographer, camera settings, and location.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
photo_id | Unique identifier for each photo. |
photo_url | URL of the photo on Unsplash. |
photo_image_url | URL of the photo image. |
photo_submitted_at | Date when the photo was submitted. |
photo_featured | Indicates if the photo is featured. |
photo_width | Width of the photo in pixels. |
photo_height | Height of the photo in pixels. |
photo_aspect_ratio | Aspect ratio of the photo. |
photo_description | Description of the photo. |
photographer_username | Username of the photographer. |
photographer_first_name | First name of the photographer. |
photographer_last_name | Last name of the photographer. |
exif_camera_make | Camera make. |
exif_camera_model | Camera model. |
exif_iso | ISO setting of the camera. |
exif_aperture_value | Aperture value. |
exif_focal_length | Focal length. |
exif_exposure_time | Exposure time. |
photo_location_name | Name of the photo location. |
photo_location_latitude | Latitude of the photo location. |
photo_location_longitude | Longitude of the photo location. |
photo_location_country | Country of the photo location. |
photo_location_city | City of the photo location. |
stats_views | Number of views. |
stats_downloads | Number of downloads. |
ai_description | AI-generated description of the photo. |
ai_primary_landmark_name | AI-generated primary landmark name. |
ai_primary_landmark_latitude | Latitude of the AI-generated primary landmark. |
ai_primary_landmark_longitude | Longitude of the AI-generated primary landmark. |
ai_primary_landmark_confidence | Confidence of the AI-generated primary landmark. |
blur_hash | Blur hash of the image. |
Unsplash Metadata Sample Table (unsplash_meta_sample)
Unsplash Metadata Sample Table (unsplash_meta_sample)
Contains image paths and their corresponding embeddings.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
photo_id | Unique identifier for each photo. |
image_path | Path to the image. |
embedding | Embedding vector of the image. |
Goals
- Obtain photo files and their metadata (e.g., photo dimensions, photographer names).
- Perform advanced queries on both structured and unstructured data using ThanoSQL to retrieve the desired metadata.
Install Required Libraries
This command installs the Pillow and matplotlib libraries, which are necessary for image processing and display.Displaying ThanoSQL Query Results in Jupyter Notebooks
The check_result function is designed to handle and display the results of a database query executed via the ThanoSQL client. It ensures that any errors are reported, and successful query results are displayed in a user-friendly format. Note: This function is specifically designed to work in Jupyter notebook environments.Displaying Images in Jupyter Notebooks
This function,show_images, displays images from URLs. It accepts either a single URL or a DataFrame containing multiple URLs. The function fetches each image using the URL, processes it using PIL, and then displays it using matplotlib.
Procedure
-
Download Datasets:
- First, we will load the datasets into pandas DataFrames and display their shapes to understand the structure and size of the data.
On execution, we get:
- This step loads the datasets into pandas DataFrames and prints their shapes to give an overview of the data size and structure.
-
Import ThanoSQL Library:
- Next, we need to import the ThanoSQL library and create a client instance. This client will be used to interact with the ThanoSQL engine.
You can find your API Token and Engine URL by following these steps:- Go to your workspace’s settings page.
- Navigate to the “Developer” tab.
- Locate and copy your API Token and Engine URL.
-
Upload Data to Tables:
- We upload the
unsplash_embed_sampletable to ThanoSQL. This table contains image paths and their corresponding embeddings.
On execution, we get:
-
This step uploads the
unsplash_embed_sampledata to ThanoSQL and retrieves the first 10 records to confirm the upload. -
Similarly, we upload the
unsplash_meta_sampletable which contains detailed metadata about the images.
On execution, we get: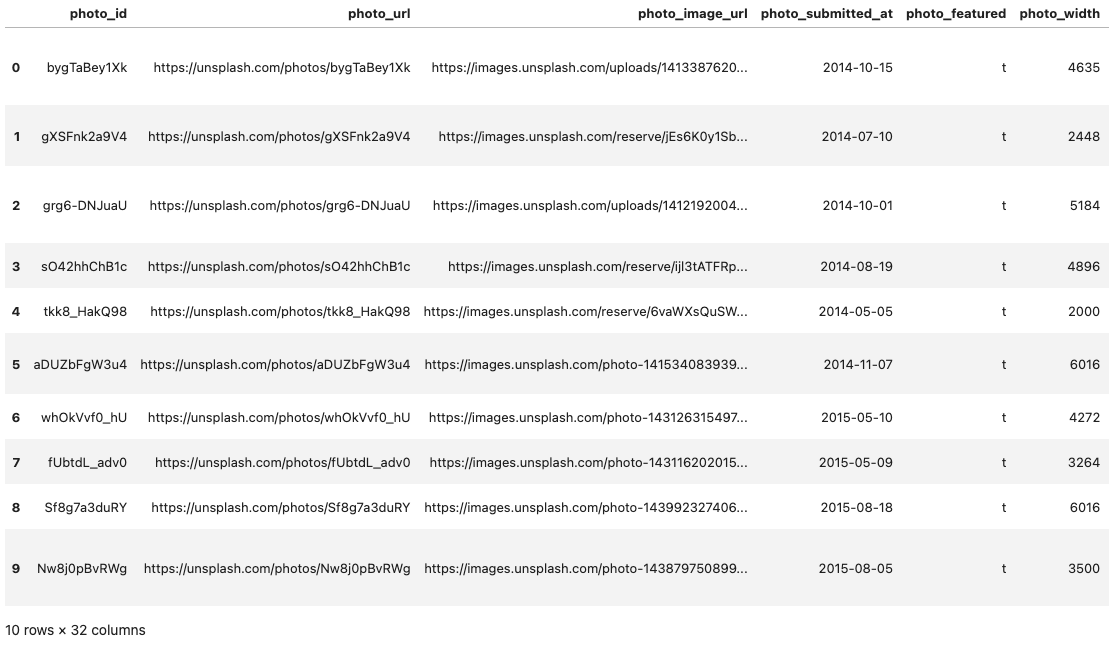
- This step uploads the
unsplash_meta_sampledata to ThanoSQL and retrieves the first 10 records to confirm the upload.
- We upload the
-
Create Embedding Column:
- To store the embedding vectors, we need to create an embedding column in the
unsplash_embed_sampletable.
On execution, we get:
- This step ensures that the
vectorextension is available and adds an embedding column to theunsplash_embed_sampletable if it does not already exist.
- To store the embedding vectors, we need to create an embedding column in the
-
Embed Images:
- Now, we calculate and update the embedding vectors for the images in the
unsplash_embed_sampletable using a pre-trained model.
On execution, we get:
- Now, we calculate and update the embedding vectors for the images in the
-
Search by Image:
- In this section, we’ll perform a similarity search using an example image. We will retrieve the embedding vector for an image of a coastal cliff and then use that vector to find similar images.
- This calls the
show_imagesfunction with a single image URL of a coastal cliff which will be used to search similar images from the sample dataset. It will display the image inline in the notebook.
On execution, we get:
- This query retrieves the three most similar images to the example image based on their embeddings with the detailed metadata for the images.
On execution, we get: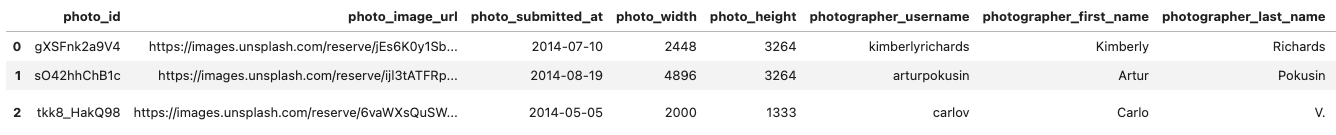
- We can now display the retrieved images using the metadata.
On execution, we get: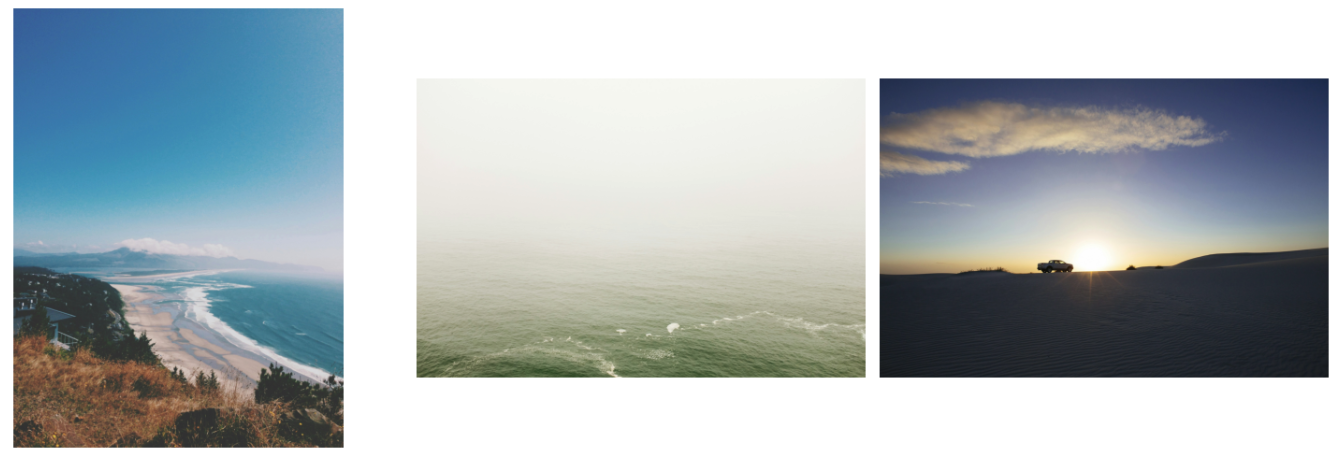
-
Search by Text:
- We can also perform a similarity search using a text description. Here, we search for the image that is most similar to the description “a photo of the desert”.
On execution, we get:
- Finally, we display the retrieved image.
On execution, we get: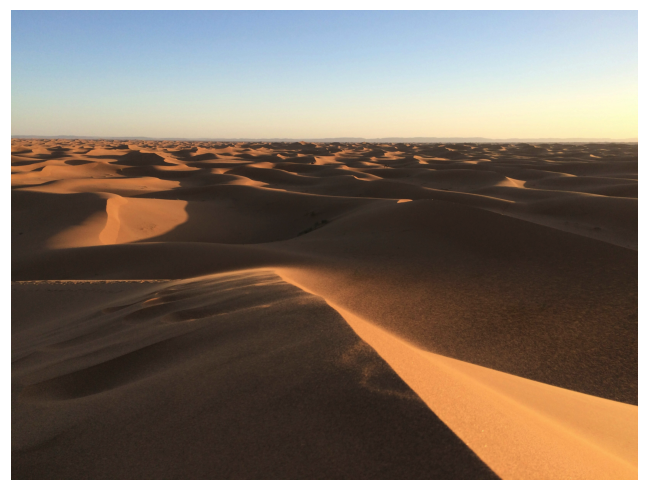
- This code fetches and displays the image using its URL from the metadata.

